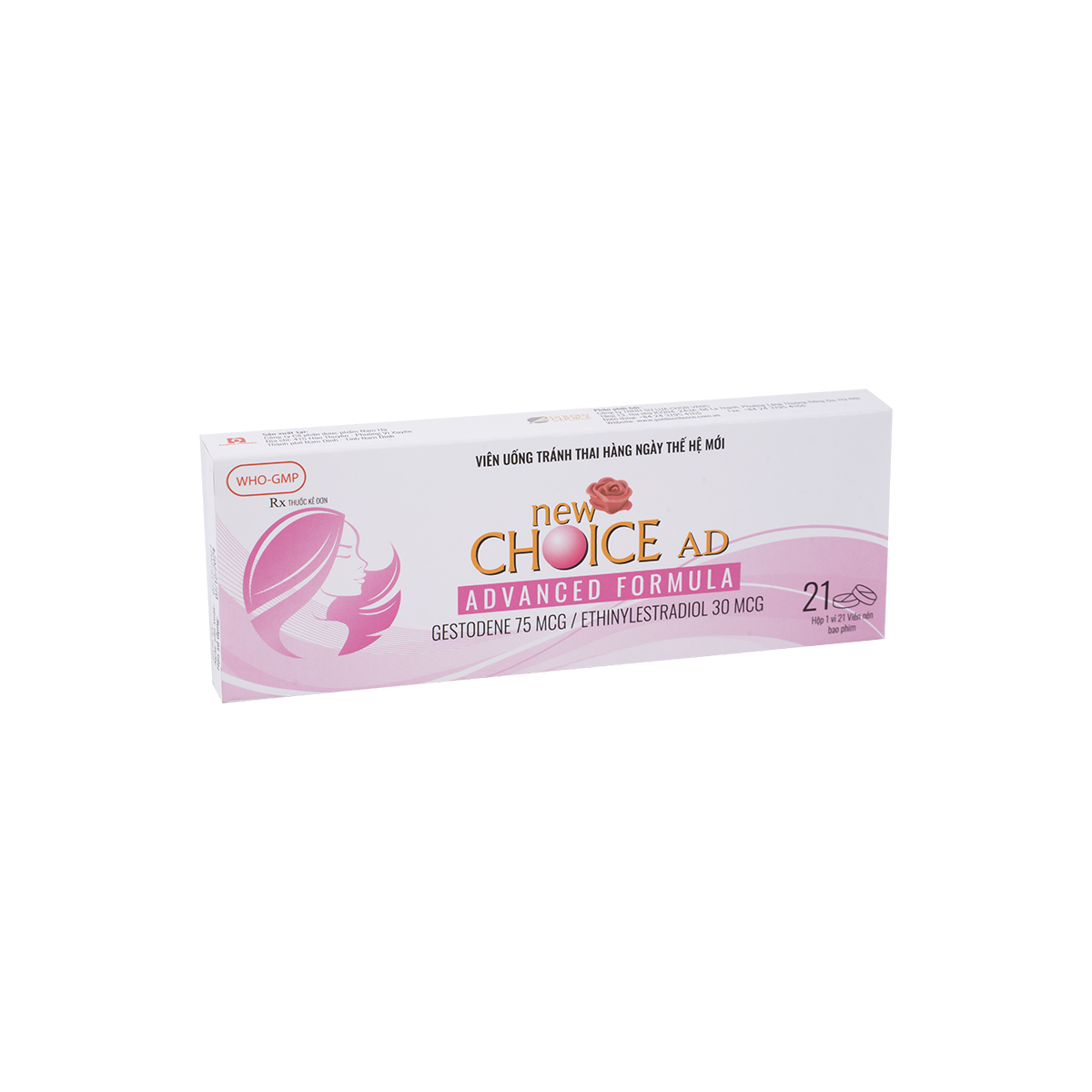
1. Indication:
Avoid pregnancy
2. Dosage and Usage:
Tablets must be taken orally in the order directed on the blister package at about the same time every day, with some liquid if necessary. One tablet is to be taken daily for 21 consecutive days. Then, take 7 days break and start a new medicine cycle.
3. Missed tablet:
– 1 Missed tablet The woman should take the last missed tablet as soon as she remembers, even if this means taking two tablets at the same time. She then continues to take the next tablets at her usual time. In addition, a barrier method such as a condom should be used for the next 7 days.
– 2 Missed tablets She should take two missed tablet as soon as she remembers, even if this means taking three tablets at the same time. She then continues to take the next tablets at her usual time. In addition, a barrier method such as a condom should be used for the next 7 days.
– Missing more than 2 tablets Please ask for Doctor’s advice.
4. Contraindications
– Venous thrombosis present or in history (deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism). – Arterial thrombosis present or in history (e.g. myocardial infarction), or prodromal conditions (e.g. angina pectoris and transient ischemic attack).
– Pancreatitis or a history of such a condition, if associated with severe hypertriglyceridemia.
– Presence or history of liver tumors (benign or malignant).
– Contraindicated for concomitant use with the medicinal products containing ombitasvir/ paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir. Contraindications of iron tablets: Excess iron in body: iron-infected in tissues, hemosiderin, hemolytic anemia.
5. Undesirable effects
– Venous thromboembolic disorders
– Arterial thromboembolic disorders
– Strokes (e.g. transient ischemic attack, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke)
– Hypertension
– Liver tumors (benign and malignant)
– Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis.
– Adverse drug reaction of iron coated-film tablet: The commonest side effects relate to gastrointestinal irritation (nausea, epigastric pain, constipation or diarrhea) – Darkening of stools may also occur.
6. Interaction with other medicaments
– The following have been shown to have clinically important interactions with contraceptive Pills: phenytoin, barbiturate, primidone, carbamazepine, rifampicin, bententan, ritonavir, nevirapine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate, Griseofulvin and Herbal remedies of St.John’s Wort (hypericum perforatum).
– For women receiving long-term therapy with hepatic enzyme inducers, another method of contraception should be used. Some clinical reports suggest that enterohepatic circulation of estrogens may decrease when certain antibiotic agents are given, which may reduce ethinyl estradiol concentrations (e.g. penicillin, tetracyclines).
– Oral contraceptives may affect the metabolism of certain other drugs. Accordingly, plasma and tissue concentrations may either increase (e.g. cyclosporin) or decrease (e.g. lamotrigine).
– The use of oral contraceptives may influence the results of certain laboratory tests including biochemical parameters of liver, thyroid, adrenal and renal function, plasma levels of carrier proteins
7. Pregnancy and lactation: No
8. Effects on ability to drive and use machine: No
9. Overdose and special antidotes:
There have been no reports of serious effects from overdose. Overdosage may cause nausea, vomiting and, in females, withdrawal bleeding. There are no specific antidotes and treatment should be symptomatic.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ